Abstract
AI as a 4.0 industrial revolution is increasingly bringing smart solutions to humans. AI brings benefits in terms of reduced energy consumption, induced cost-effectiveness, reduced operational risks, and increased performance matrices. The review will elaborate on how AI is revolutionizing various industries, including food, drug discovery, e-commerce, and chemical industries, by offering smart solutions. Resulting in reduced energy consumption, enhanced cost-effectiveness, mitigated operational risks, and improved performance metrics. Additionally, the results section will also elaborate on AI applications extended beyond these major sectors into numerous others, such as cosmetics, tourism, automobile, mechanical, environmental management, gaming, textile, entertainment, and enzymatic design industries. The integration of AI facilitates efficient structuring, administration, design, productivity, manufacturing, promotion, and accessibility of industrial products. However, its utilization remains under-regulated and predominantly limited to modernized economies, necessitating broader integration across small-scale, medium-scale, and large-scale industries in both developing and developed countries. Collaboration among academics, researchers, industrialists, economists, administrative personnel, technologists, and environmentalists is crucial to foster a more sustainable, energy-efficient, economically viable, and safe integration of AI across various industries worldwide.
Graphical abstract

Application of AI in Industry.
Keywords
Artificial intelligence
AI and industrial applications
Machine learning
Internet of things
AI and food industry
AI and E-commerce
AI and drug discovery
AI and chemical industry
AI and COVID-19
1. Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming various industries by providing new solutions, enhancing the efficiency, and reducing costs [1]. Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem solving, perception, decision-making, and language understanding [2]. AI systems use various techniques, including machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, to analyze large amounts of data and make predictions or decisions based on that analysis [2], [3]. Some examples of AI applications include virtual personal assistants, self-driving cars, fraud detection systems, image and speech recognition, and medical diagnosis and treatment [4]. AI is a rapidly advancing field that can transform many industries and aspects of everyday life.
Artificial intelligence along with some other revolutionary measures such as machine learning, and the Internet of Things is together getting the attention of modern industrialists. AI holds the potential to replace, replicate or benefit along with human intelligence [5]. This is because the industries are more concerned about the challenges associated with process modeling, product and mechanism optimization, quality control strategies, fault detection and risk diagnosis [5]. These aspects are associated with the sustainable aspect of modern economies that inculcate insights about social, economic, and environmental impacts analyzes along with aspects of sustainability implications [6].
Hundreds of billions of dollars are being spent worldwide for the successful implication and integration of AI in several industries, especially in the developed world of Europe and countries like China, America, Japan, and Korea [7], [8]. New entrepreneurial setups are also most often linked with AI-based technology owing to the diverse fields of operability, design, and creative programing [9]. However, developing nations are still lagging owing to the meager and poor management of natural and human resources that keep them on the back foot for actualizing industrial AI applications [10]. The pertinent need is to ascertain by all industries around the globe that AI is the new face of the technological generation of the 21st century. Thus, industrialists need to cooperate and spend excessively in the field of AI-associated industries in the coming years to meet the needs of the rising population in the coming years. Industrial growth at an ever-fast pace could accustomed to the prevailing age of technology [11], [12]. However, industries today face an overburdening challenge in terms of global competition, unpredictable customer experience and needs, and continuously increasing environmental concerns. These concerns are enough for the manufacturer to deviate focus on improved and efficient utility products so that these products are read to consumers in a reasonable time with lower costs [8]. The best possible solution lies in artificial intelligence by maximizing its useful implications and minimizing the risks and threats associated with artificial intelligence applications in industries [1], [13]. Fig. 1.
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1Overall, AI is transforming industries by providing innovative solutions that enhance productivity, efficiency, and customer experience. The findings will help readers, researchers, managers, and developers to evaluate, analyze, integrate and use the most sustainable AI technologies in their relevant industry of study [1], [2], [4]. Ultimately, the study will bring into account the current challenges and future directives for successful AI-industrial consensus establishment. In the review of the status, it is not wrong to predict that AI-industrial applications would become a compulsory field of study for future generations [12]. AI is truly the fourth industrial revolution affecting our lives with great improvements and automation. It directly increases lives through industrial upgradation and advanced automation. It affects various aspects of human life such as healthcare, automation, connectivity, transportation, social integration, economic stability, cultural renovations, and political interdependencies [2], [3], [7], [12]. In short, it creates a world of globalization. This paper is a directive for the advantages, opportunities, limitations, formulations, and challenges to truly implement the appropriate AI technologies in industrial sectors for the ultimate benefit of present and coming generations.
The manuscript offers a novel contribution by identifying data and methodological gaps in prospective AI applications across various industries, particularly in developing countries. It presents a conceptual framework and theoretical guidance for selecting the most beneficial AI methods and technologies to enhance impact assessment and productivity in different sectors. Additionally, the review compiles a comprehensive study focusing on diverse AI-linked industries and highlights future research directions to improve AI integration in the global industrial sector. By bridging the theoretical underpinnings of AI applications with practical implementations in modern industries, the study addresses the evolving trends of intelligence, automatization, and digitalization, which are pivotal for facilitating technical advancements and automation. Overall, this manuscript provides valuable insights into the potential of AI in shaping the fourth industrial revolution. This study creates a bridging link between the theoretical underpinnings of AI applications and practical applications in modern industries. Intelligence, automatization, and digitalization are uncertainly the mainstream trends in the contemporary and future industries for the linked technical facilitation and automation [6], [7], [12]. The findings summarized in this study are based on perspective, importance, and most practical output to create the true face of the fourth industrial revolution.
2. Materials and methods
The data for this comprehensive review have been gathered from the most diverse research journals, recent publications, and most cited studies. Most journals with specifics on nanotechnology have made up part of this study.
2.1. Search strategy
A systematic research strategy has been adopted to gather data from online sources, including mainly Google Scholar, while some other platforms like Pub Med, NIH (National Library of Medicine), Web of Science, European Database, Springer, and Embase databases have also been given consideration. As the study mainly incorporates the data regarding artificial intelligence in industries, the major research items were “artificial intelligence”, “AI and industrial applications”, “machine learning”, “internet of things”, “AI and multiple industries”, “and some other linked search terms. After a thorough analysis of the dates, abstracts, titles, and journals of research publications, they have been included in this review. Only data of English origin have been included here. Moreover, this review has mostly reviewed studies conducted in the last five years (2018–2023), to elaborate on the fast pace of artificial intelligence in the past few years.
2.2. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The study includes original research articles, sections from books, letters to the editors, short and lengthy reviews, and some case studies published recently. The available data has been immense, but we tried limit the data to 100 studies from which the interlinked data have been gathered. The remaining studies show overlapping data. A multipronged view has been presented to show how different industries are benefiting from the field of artificial intelligence and industrial conjugate.
3. Results
The following section gives a comprehensive overview of the applications of artificial intelligence (AI) and associated concepts such as machine learning (ML) and the Internet of Things (IoT) in some important industries. A summary figure of these applications is covered in the graphic abstract version at the beginning of this review article.
3.1. Artificial Intelligence- general industrial applications
Industrial Revolution 4.0 involves the convergence of AI-based intelligence and computer technologies at one point to create a smart factory system. The system works to develop focused intelligent networks, machines, and functions like humans. AI, ML, and IoT along with other interconnected applications form the basis for this industrial revolution [14]. These technologies help industries in multiple beneficial ways with hundreds of applications in different industries. If a general approximation is conducted, AI technologies create work efficiency, time-saving, cost-effective, production processing, modeling, qualitative analyses, defect analyses, waste management, and revenue projection, which together dictate better production and consumption, enhanced satisfaction, and improved workplace experience for industrialists, consumers, and workers respectively [7], [13], [14], [15], [16].
As a result, businesses and industries can schedule advanced manufacturing lines with a major advancement in supply chain fluctuations and management without getting prone to human error and interface [17]. AI helps to accelerate procedures and improve the overall precision of different processes in industries in terms of efficiency, protection from hazards, facility and human resource management, logistic actions, transport help, labor-intensive facilities, and manufacturing capabilities enhancement [6], [8], [12], [15], [18].
The different ways in which AI helps industries in performing better may include the help in the performance of routine tasks via robotic systems and automatic processing. Robotic systems are well established with the ability to track the accuracy and efficiency of procedures in random environments [19], [20], [21]. Another application of AI in the industry includes the help in planning, production, and demand cycle assessment and forecast, which helps in both natural and human resources efficient management [21]. ML technologies help to handle large inventory volumes and avoid cash and stock exchange problems [22]. AI also helps in sustainable manufacturing and refined processing. Additionally, it creates product awareness for asset efficiency and product personalization, and differential permutations for attracting consumer interest in products [3].
Another important application comes in the form of better monitoring and safety profiling for common-use products. It allows the staff to monitor through scanning and contract tracing technologies [23], [24]. AI has allowed for long-term solutions for root cause identification and error detection in ongoing processes with a reduction in downtime and guarantee of the higher ending quality of the process and product [25]. It provides the appropriate information that sometimes may be missed or misinterpreted by humans. AI and ML try to overcome the microscopic defects and the resulting accurate information sharing [25], [26]. As elaborated earlier, its implication in designing and manufacturing remains the topmost application. AI performs iterative design processing based on algorithms and comprehensive designs to officiate the processing and design methods in terms of time limits, budget constraints, and design of product specifications [27], [28].
AI technologies also conduct defect detection with the help of digital technologies such as cameras, video cameras, mobile and scanning devices, and teachers’ apps [29], [30]. Moreover, it encourages the younger slot to come forward with their own set of revolutionized methods; however, the risk of ill-uses and wrong uses of AI in industries is persistent [31], [32]. However, the quality assessment procedures of AI create a platform for quality assurance and process optimization product analyses and computer-based vision detection [33], [34]. Process optimization such as machine education language modeling, machine vision, and robotics-based recognition system-based technology is conducted cleanly and optimally [22], [34], and [35]. With the help of the latest developments in ML production, market, and inventory management has become easier with robotics. Smart management tries to overcome the repeats linked to error-prone situations if left to humans alone [17], [36].
3.2. Drug discovery and development- AI, IoT, and ML
The drug discovery industry involves the identification and development of new pharmaceutical compounds to treat various diseases and medical conditions. It encompasses activities such as target identification, lead optimization, and clinical trials [37]. AI technologies are revolutionizing the drug discovery process by accelerating research and development efforts, reducing costs, and improving the success rate of drug candidates. These technologies enable tasks such as virtual screening, molecular modeling, and predictive analytics. Additionally, AI-powered platforms help in identifying drug interactions, predicting drug efficacy, and optimizing dosing regimens [7], [8], [9], [10]. However, challenges such as data scarcity and regulatory hurdles may arise with the use of AI in drug discovery. Despite these challenges, AI contributes to societal advancement by facilitating the development of novel therapeutics, improving patient outcomes, and addressing unmet medical needs [38].
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become an increasingly important tool in drug discovery and development due to its ability to process vast amounts of data and make predictions based on that data [37]. There are several applications of AI in the field of drug discovery and development, including target identification in which AI algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify potential targets for drug development [38]. By analyzing genetic, clinical and chemical data, AI can identify novel targets that may not have been discovered through traditional screening methods [39]. Similarly, drug designing is carried out by AI that can be used for computer-assisted drug design, allowing researchers to create virtual compounds and test their potential efficacy before conducting experiments in the lab [40], [41].
Another application involves toxicity prediction where AI can be used to predict the potential toxicity of a drug before it is tested in animals or humans [42]. This can help researchers prioritize that compounds to move forward with and potentially save time and resources. Additionally, clinical trial optimization is a field-based AI application where AI can analyze patient data from clinical trials to identify patterns and predict which patients are most likely to respond to a particular drug [15], [43]. This can help researchers design more efficient and effective clinical trials. Moreover, the areas of regenerative and personalized medicine are where AI can analyze patient data to predict which treatments are most likely to be effective for individual patients [44]. This can help healthcare providers make more informed treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes Fig. 2.
 Fig. 2
Fig. 2Medicine development remains the hind bone of the healthcare system, which is being operated since the very beginning of scientific development [45]. With its diverse applications, AI has become an important tool in the hands of researchers, students, pharmacists, and clinics to delve deeper into the drug delivery implications [46], [47]. AI tools make the drug discovery program efficient, accurate, up-to-mark, cost-effective, error-free, and swift [33]. AI makes the drug development process easier by eliminating extensive clinical trials with the alternative of simulations and modeling, which allows scientists to study the molecules more comprehensively [48]. It allows industrial drug manufacturing with enhanced quality management, end–product characterization, and fixed and changing operational conditions as per need [13].
AI has augmented the pharmaceutical industry with novel technologies and principles of investigation, characterization, and delivery approaches. With the rising healthcare budget, more population, and the rise of multiple diseases, AI allows large-scale manufacturing, handling, packing, and discovery of drug products [38], [39]. However, the mainstreaming of AI-based technologies and incorporating them into the therapeutics world with general acceptability, accessibility, and credibility of consumers remains a challenge for researchers and industrialists [3], [37]. Besides the usual “one medicine for the whole population“ strategy scientists are looking for alternatives in terms of personalized and more efficient systems of drug discovery and delivery [15], [42]. AI thus works by helping improved genomics, diagnostics, modeling, analytical instruments, and delivery tools to work more precisely. The drugs are compared with human biology to make them more specific and efficient [43], [44].
AI is helping medical practitioners, specialists, surgeons, nurses, and medical faculties to assist in patient care, medical operations, surgeries, disease prediction, diagnosis, and treatment predictions [42], [44], and [45]. It also helps to overcome the complications associated with treatment by allowing righteous analyses of conditions, dosages, and procedural specifications [5], [18]. Additionally, the biggest achievement of AI in healthcare and drug discovery programs includes the analysis and management of big data with the help of supercomputers. Big data collection and management also become useful for researchers and in-silico models to use data for in-depth research and experimentation [37], [49]. AI programs and big data acquisition side by side help to make drug manufacturing efficient with a collective procedure of extraction and collection of scattered data and its configuration followed by uniform formatting and finally the data analyses on various platforms for output management with the help of upgraded computerization [41], [50], [51].
The exact mechanism of drug discovery mostly follows 4 procedural steps, the design of the polypharmacology, analyzes, drug repurposing, and the final drug screening against the population [16], [38], [39], [41]. All these steps are progressively being assisted with AI technologies to assist the clinical implications. Interpretations based on the results dictate the efficiency and accuracy of the result predictions and practices. It reduces the need for clinical trials, which covers both the ethical and financial concerns of the healthcare industry [38], [40]. Overall, AI has can revolutionize the drug discovery and development process, making it faster, more efficient, and more effective. However, AI is not a replacement for human expertise and collaboration between humans and machines is necessary for successful drug discovery and development [15], [41], [43].
3.3. AI in the food industry
The food industry involves the production, processing, and distribution of food products. It encompasses various sectors, including agriculture, food manufacturing, and food service. AI technologies are increasingly being applied in the food industry to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure food safety [35]. These technologies enable tasks such as crop monitoring, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization. Additionally, AI-powered tools help in food quality inspection, allergen detection, and shelf-life prediction. However, challenges such as regulatory compliance and consumer trust may arise with the adoption of AI in the food industry [52]. Despite these challenges, AI contributes to societal well-being by promoting sustainable agriculture, reducing food waste, and ensuring the availability of safe and nutritious food for consumers.
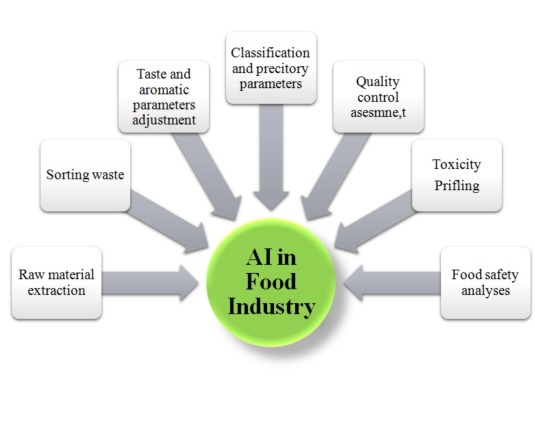
The ever-increasing population burden increases the implications of more and more food supply, and this necessitates the systemic functionality in food industries. AI, ML, and IoT help to overcome these issues in terms of raw material extraction, sorting waste, classification and predictory parameters, quality control assessment toxicity profiling, and food safety analyses among others [49]. AI technologies also help to increase awareness among the masses regarding food knowledge, food properties, commercialization, and production processes for greater consumerism and acceptability among the masses [52]. The use of AI in the decision-making process and knowledge-based expert systemic analyses during different industrial processing such as winemaking, fermentation supervision, wheat and rice sorting, fruit handling and sorting, artificial flavoring, and conditions optimizations in different beverages among others [35], [52].
AI in food industries creates value addition through process design, safety, nutrition value, quality level, safety analyses, quality management classification purposes, and risk assessment that enable the food quality certificates [53], [54]. The ranking of sensations and sensory attributes based on flavors, smell, and color have been made easier by Ai modeling [49]. The sensory systems are based upon the combined effects of electronic noise, tongue, and visionary systems for controlled thought computers, scanning technologies, and infrared spectroscopy among other technologies directly linked with AI applications [49], [55]. These digital sensory tools allow smelling, colors, shapes, defects, and size-based analyses of food items. Moreover, other AI technologies enable the detection of food components and properties of prepared, packed, and preserved food materials Fig. 3 [35], [54].
 Fig. 3
Fig. 3As elaborated earlier, the implications of AI in food industries are continuously increasing with population and consumerism and are predicted to further rise in the future. The major element that has contributed as a reason and outcome for the increasing food production is the AI and computer-based technologies that together dictate the natural revolution 4.0 [6]. This technological revolution helps to inspect food industry-based consumer complaints and rectify them efficiently to resolve and dictate better human acceptability and behavior toward modern food items and processed food products [35], [53].
3.4. E-commerce industry and AI
The e-commerce industry involves buying and selling goods and services over the internet. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including online retail, digital marketplaces, and electronic payments. AI has revolutionized the e-commerce industry by enabling personalized recommendations, predictive analytics, and targeted marketing strategies. These technologies enhance the shopping experience for consumers, increase sales for businesses, and streamline supply chain management processes. However, challenges such as algorithm bias and data privacy issues may arise with the use of AI in e-commerce. Despite these challenges, AI contributes to societal progress by creating job opportunities, promoting economic growth, and expanding access to goods and services.
The applications of AI, ML, and numerous other technologies in e-commerce, business, and finance industries are probably the most implicit ones [56]. AI lays the foundation for e-commerce industries. Applications in different formats will be briefly touched upon here. First, the use of chat bots made through AI and machine learning modules has boosted the e-commerce accessibility and demand on different websites that directly coordinate with client satisfaction and happy experience, good deliverability, and maximum profit, by acting like humans [56]. They learn, coordinate, answer, devise solutions, and transfer messages based on previous data analyses. Similarly, image search technology is yet another useful application of AI in the commerce industry where image searching on websites becomes easier. They allow image processing, formatting, editing, picture enhancement, and improved visual representation for the greater satisfaction of customers [22].
Another important benefit of AI and e-commerce duality is the handling of large customer and product data [37]. The different AI algorithms enable product sales, consumer ratings, resource optimization, sales maximization, product resourcing, marketing, purchase product analyses, and profit maximization to benefit both consumers and manufacturers [3], [19], [49]. Additionally, it allows the recommendatory versions of machine learning to identify consumer choice based on historical data and product preferences to attract further consumer interest in similar products [8], [57]. AI technology automatically and efficiently catches consumer interest through search patterns to recommend the latest trends on similar products and goods, thus boosting sales to companies and improving customer satisfaction. The past and present sales analyses help regulate future sales management and inventory maintenance [56].
Yet another beneficial application of AI in e-commerce is the application of cyber security procedures for detecting flaws, breaches, financial frauds, hacking, and security appropriations to make e-commerce platforms safe for consumers [56]. The greater concerns of financial fraud in financial institutions are well managed throughout the world with the help of AI algorithms [22]. This may sound like just another benefit but has implications lying in terms of billions of dollars saved around the world [2]. Similarly, artificial intelligence programs and screen resumes help users in discovering routine patterns and arranging operations. The robotic systems and AL bots help to conduct video interviews; screen tiering, candidate selection, behavioral assessment, and employees' dedication to the companies [4], [58]. Mooar's innovative methods of AI can be used for education, training, testing, and ability analyses for delivering the best client acquisition options [10], [58], [59]. Moreover, AI techs also help to moderately handle pricing, boost sales, and increase the market basket for better industrial growth. Technological assistance through underwriting, portfolio management, loan management, and credit scoring allows further data predictions for financial companies to encounter the prevailing economic challenges Fig. 4 [59], [60], [61].
 Fig. 4
Fig. 4These benefits of AI in e-commerce come along with some challenges that need to be properly managed for more pros of the AI-e-commerce complex. The first is the budget inflictions in companies that limit their ability to successfully use AI help [56], [62]. Thus, financial institutions set prior goals to set reasonable expectations and implications of AI in business modeling and service provision. Although the challenges are there, AI platforms still hold an optimistic outlook for the future of e-commerce, finance, and the business sector in terms of recommendation approaches adoption for goods sales, security enhancement, customer sentimental analysis, and improving customer service provision [56]. Moreover, machine and deep learning technologies can help industries and e-commerce platforms forecast production management with proper regulation of data diversity that may enable full-scale optimization and digitalization of financial systems in the future [19], [22].
3.5. Artificial intelligence in the chemical industry
The chemical industry involves the production, processing, and distribution of various chemical substances. It plays a crucial role in manufacturing products ranging from pharmaceuticals and fertilizers to plastics and paints. AI technologies are increasingly being integrated into the chemical industry to optimize processes, improve efficiency, and enhance safety. These technologies help in predictive maintenance, quality control, and real-time monitoring, leading to reduced production costs and improved product quality. However, challenges such as data privacy and security concerns may arise with the adoption of AI in this industry. Overall, the integration of AI in the chemical industry contributes to societal welfare by fostering innovation, reducing environmental impact, and ensuring the safety of chemical products.
The chemical industry has diverse outputs that are compiled with several other industrial implications. Therefore, these apprehension about AI application in the chemical industry is likely a discussion of several connected industries where AI indirectly contributes to significant applications. The three important perspectives of AI application in the chemical industry involve the areas of research and development, operational management, and processing of chemical plants [63]. In the research & development (R&D) sector AI is an essential tool for innovation, sustainability-driven development modeling, and predatory frameworks for future research digests [64].
AI on a small scale helps to regulate chemical reaction optimization and chemical synthetic design elaboration. It also helps to regulate the catalyst and enzymatic modalities, time, amount, and application guidelines, and appropriation of reaction conditions and sustainable chemical materials development for different industries [65], [66]. Moreover, the overall workload management, operational and work environment satisfaction, and improved digitalization of research labs are governed only by the combined applications of AI, ML, and IoT along with ICT technologies [67], [68].
In the case of unit operational management, which compromises the synthesis and separation processes for chemicals, AI improves the overall work conditions such as the operational conditions of combustion, distillation, compression, evaporation, reaction, and crystallization [63], [68]. Moreover, the technical regulations related to the yield of the products, its quality assessment, and the textural analyses are some of the steps where AI plays an important intelligent control of operations [64]. Similarly, in the case of processing and chemical plants, AI pays the conforming characteristic of engineering sense. The different algorithmic diversions involving deep neural networks, transfer learning, deep learning, machine learning, and convolutional neural networks are some of the tools AI uses to address process-controlling problems in chemical industries [15], [63], [64], [69]. AI also allows risk management, plant design, quality assessment yield control, cost analyses, and eco-designing in chemical plants, which are of utmost importance for sustainable industrial development. These implications increase the healthcare, safety, economic, social, and environmental stability of the industrial community as well [17].
Furthermore, in the case of supply chain management, different entities such as suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and consumers are integrated via AI-based technologies developing around the final product [17], [37]. AI helps in manufacturing, delivering, and transporting these products in the supply chain cycle. Through the characteristics of artificial designs, planning, data amendment, and conditional optimization, the chemical industries, and AI together brings about efficient supply chain management with good economic aspects [22]. Algorithms such as genetic algorithms, heuristic algorithms, case-based reasoning, and agent-based modeling help regulate the systematic supplier selection, manage disruptive, supply chain modeling, and material sections for the efficient running of supply chain series [30], [59].
3.6. Artificial intelligence – And the era of new normal post Covid-19
The Covid 19 pandemic impacted the whole world in different interconnected ways. It creates a likely new normal system where everyone and everything got affected by the pandemic yet developed normalcy with it in the form of a new normal [43]. During this era AI played an effective role in managing fields of healthcare, manufacturing industries, retail, food services, education, media entertainment, travel and tourism, banking, and e-commerce among various other domains of community [30], [70]. However, the diverse implications of AI during the post covid era proved its significance along with the ICT and computer-based technologies for the management of social, political and economic affairs in the coming years [31], [70]. During the Covid-19 pandemic, artificial intelligence was instrumental in the fight against the virus; some of the practical implications of AI during the covid-19 and post-covid era are discussed in a summarized tabular format below (Table 1). Artificial intelligence has proven to be a valuable tool in the fight against COVID-19, and it will continue to play an important role post-pandemic in helping to address some of the world’s most pressing issues [31], [71], [72], [73], [74].
| Sr. no. | Different Applications of AI | Applications specific to Coved and Post Covid era |
|---|---|---|
| Early Detection and Monitoring | AI-powered systems and models were used to detect early indications of COVID-19 outbreaks, monitoring the spread of the virus, and predicting its trajectory. | |
| Contact Tracing | Health authorities used advanced AI-powered techniques to aid contact tracing efforts by analyzing various data sources such as GPS, medical records, and cell phone information. | |
| Diagnosis and Treatment | AI-powered systems have helped medical professionals to diagnose and devise treatment plans for COVID-19 patients quickly. | |
| Vaccine Development | Artificial Intelligence has played a critical role in vaccine development. AI models have aided scientists in developing vaccine candidates by analyzing genetic sequences of the virus. | |
| Telemedicine | Artificial Intelligence-powered telemedicine applications will enable doctors and patients to connect online, thus reducing hospital visits significantly. | |
| Enhanced Cyber security | AI-powered cyber security systems will help prevent cyber-attacks, and data breaches, and secure sensitive data. | |
| Automation | AI-powered automation will enable businesses to streamline operational processes, paving the way for increased productivity, cost savings, and efficiency. | |
| Personalized Education | With advancements in AI-powered learning technologies, educators will have the power to personalize the learning experience to students individual needs. | |
| Autonomous Vehicles | AI-powered autonomous vehicles will revolutionize transportation, making it safer, greener, and more efficient. |
3.7. Some other applications of AI in different industries
Since the review is not able to cover the extensive details of each industry in detail for the wide spectrum and diverse AI applications in each sector, we would like to give an overview of AI applications in some of the common industries for the understating of over readers and for the apprehension regarding the importance of AI in industries in the present era (Table 2).
| Sr. no. | Industries | Applications of AI | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI in cosmetics Industry |
|
[76], [77] | |
| AI in tourism industry |
|
[33], [78], [79], [80], [81] | |
| AI in automobile and transport industry |
|
[27], [61], [82] | |
| AI in mechanical |
|
[20], [27], [50], [61], [82], [83] | |
| AI in environmental management |
|
[2], [13], [25], [84], [85] | |
| AI in the gaming industry |
|
[62], [86], [87], [88], [89] | |
| AI in Textile Industry |
|
[20], [23], [69], [90], [91] | |
| AI in entertainment industry |
|
[19], [33], [34], [76], [87], [92], [93], [94] | |
| AI in ICT |
|
[1], [95], [96], [97] | |
| AI in enzymatic design |
|
[65], [66], [67], [68] |
3.8. Future of AI industrial applications
The larger picture is that AI has massive industrial applications that cannot simply be averted or replaced but can only be modified and upgraded further to benefit the industries more than at present. The industries of developing countries still hold a large gap where AI technology can be brought in and applied to revolutionize the economy of such countries to compete with the industrially transformed world of today [1]. AI leads to changes in productivity patterns, business model upgrading, lower maintenance costs, less labor intensive, better waste management, and sustainable industrial growth and development [6]. Moreover, supply chain management with stock market efficiency can be well-synced to maintain a technology-renowned industrial output [7]. This mixture of adaptive machinery and refined software dictates the future of industries in the coming years. With these implications, many industries want to operate AI in industries to improve quality, management, standardization, maintenance output, and sustainability-driven progressive rationalization and automation in the respective industrial lines [8], [12].
AI in industries has radically changed markets and consumer patterns over the years. Owing to these benefits, many different industries apart from the usual ones are incorporating tools, procedures, devices, equipment, and technologies associated with AI, ML, and IoT. This is because of the increasing reliance on AI technologies that combine processes, machines, data, and operations to bring the best outcomes for humans [9], [10], [11]. The system combines the work of sensors, transmitters, digital devices, technologies, computers, and cloud servers to create a better operation with better quality, cost, product, delivery, and consumer satisfaction [25].
Various industries have been transformed, including the food industry, healthcare industry, pharmaceutical industry, life science, automobile, textile, cosmetics, manufacturing, and entertainment industries [5], [6]. These AI technologies connect practical concepts of biology, robotics, information technology, computer science, smart systems, mathematical modeling, and other scientific paradigms of modern life [7], [8]. Thereby creating a virtual cyclic flow of the production-consumption cycle as per the needs of consumers. This subjective knowledge enables predictive analytics to run smoothly in industries of various kinds. Thus, from manufacturing to production, transport, delivery, usage, and evaluation of consumer satisfaction AI is the fuel of modern industries [9], [19], [62], [90], [94]. It enables such operations in the business world, where humans cannot easily get access otherwise. It removes human-prone errors, prejudices, biases, and miscalculations that could avert the right decision-making and productive outcome for the greater good of society. Further dimensions of AI have now been coming to the surface such as IoT, edge computing, block chain, and augmented reality (AR), which are expected to be marketed soon in coming years to have a smarter society, intelligent businesses, and productive industries [21], [62].
4. Conclusion
AI-based industrial applications have transformed the world with paradigm-shifting through the automation of different processes. AI is completely integrating industries through real-time applications such as data management, manufacturing, and production. From raw materials to the final product and from product to consumer satisfaction, a cycle of upgraded industries has been possible only by AI applications in the age of industrial revolution 4.0. This article has shed light on the transformative impact of artificial intelligence (AI) across diverse industries, including the chemical, e-commerce, food, and drug discovery sectors. By identifying data and methodological gaps in AI applications, especially in developing countries, and presenting a conceptual framework for selecting the most beneficial AI methods and technologies, this review has contributed new insights into the integration of AI in industrial settings. Additionally, the comprehensive study compiled in this article emphasizes the importance of bridging theoretical underpinnings with practical applications, thereby fostering innovation and efficiency in modern industries. Through the exploration of AI's role in optimizing processes, improving productivity, and enhancing safety measures, this article has provided valuable guidance for future research directions and industry practices. By addressing challenges such as data privacy and regulatory compliance, this review underscores the need for collaborative efforts among stakeholders to ensure the responsible and effective integration of AI across global industries. Overall, this article serves as a roadmap for harnessing the full potential of AI to drive economic growth, promote sustainability, and enhance societal well-being in the fourth industrial revolution and beyond. This will help researchers to make alternative solutions to gather sufficient knowledge and information and decision-making power for future investments and develop the big picture associated with AI-based applications for the sustainable development of industries.
Funding
K.M.’s work is supported by SURE Plus grant by United Arab Emirates University, UAE.
Yasir Waheed is a member of Pakistan Academy of Sciences, which is a pool of highest scientific talent in Pakistan. Dr. Yasir is included in the list of Top-2% highly cited researchers of the world in the last four consecutive years (2020, 2021, 2022, 2023). He is the recipient of several local and international awards.
© 2024 THE AUTHORS. Published by Elsevier BV on behalf of Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University.